Admat®C/Admat®Z
VOC Removal Technology | Concentrating Units
What is VOC removal technology?
We offer a wide variety of environmental protection devices, covers from various exhaust gas treatment systems and dust collectors to wastewater treatment systems. This section introduces exhaust gas treatment system to dispose organic gases from various plants.
What is concentration unit?
- Adsorption and desorption technology for concentrating volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Prior learning technology for determination of optimal operating status with variable rotation speed and velocity.
- Want to prevent air pollution
- Want to reduce CO2 and enhance energy efficiency
- Want to make the best use of limited spaces
Admat® C
Overview
This system cleans up organic solvents, cleaning solvents, and malodorous gases from painting, printing, semiconductor, electronic parts, precision machinery, and chemicals factories, using adsorbing materials and oxidative decomposition equipment.
Fibrous activated charcoal is used as the adsorbing material.
 Admat® system C model (adsorbing material: fibrous activated charcoal)
Admat® system C model (adsorbing material: fibrous activated charcoal)
Record of Awards
- Awarded the 19th (FY1998) Japan Machinery Federation (JMF) Presidential Prize for Excellence in Energy-saving Machinery.
- Awarded the FY1998 Japan Gas Association Prize in Technology.
Features
-
Lower initial & running costs
Admat® uses less activated charcoal and requires a lower initial cost than traditional adsorption system.
Fibrous activated charcoal used as the adsorbent is less expensive because it involves no complex secondary processing, and the replacement cost of the adsorbent is one half to one third of that of traditional system. -
Energy & space saving system
Because only the charcoal with a smaller thermal capacity is heated, the entire energy of the hot air for restoration is efficiently used for desorption, thus providing a higher concentration rate. Both the concentration and post-treatment units are compact and lightweight.
-
Support for small to large volumes of gas
Admat® can support a wide variety of exhaust gas conditions, ranging from low concentration and small volume to large volume.
Increasing or decreasing the number of cassettes can also address a change in gas volume. -
Safer operation
Less use of activated charcoal means a smaller amount of adsorbed solvent, allowing for safer operation.
Spetifications
Structure of Admat® C model
Admat® uses fibrous activated charcoal as its adsorbent.
This is processed into a felt-like sheet which is wrapped around a wire-netting pipe (Figure 2) to form a cassette and which is then attached to a rotor.
Rotating slowly, the rotor continuously induces simultaneous adsorption and desorption.
Adsorption occurs when untreated gas penetrates from the outside of the cassette to the inside, as shown in Figure 3a, and desorption (restoration) is induced by letting hot air at about 130°C flow from the inside to the outside, as shown in Figure 3b.
A change from adsorption to desorption occurs when the cassette arrives in the specified desorption zone at the top of the rotor, as shown in Figure 1.
Desorbed solvents are finally treated and made harmless (for example, deodorized) with post-treatment systems such as Catabrrn® and RTO.
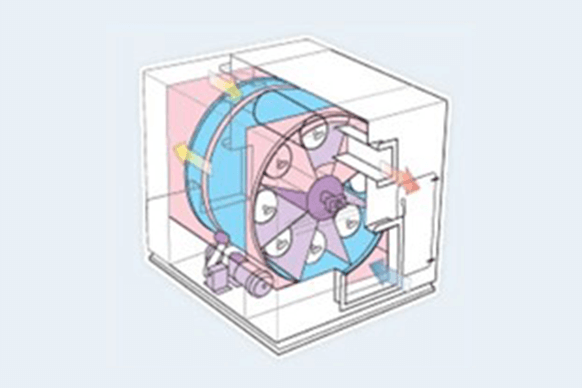 Figure 1. Admat® C model (Concentration unit)
Figure 1. Admat® C model (Concentration unit)
 Figure 2. Cassettes
Figure 2. Cassettes
Performance and Industrial Application of Admat®
Admat® delivers varying treatment efficiencies, depending on the type of treated gas and its concentration. Figure 4 shows an example.
A gas with a low concentration is highly concentrated to achieve higher treatment efficiency.
The concentration unit of Admat has an extremely low air resistance, or pressure loss, as shown in Figure 5, contributing to a more compact and lightweight system and requiring less power for air blowing.
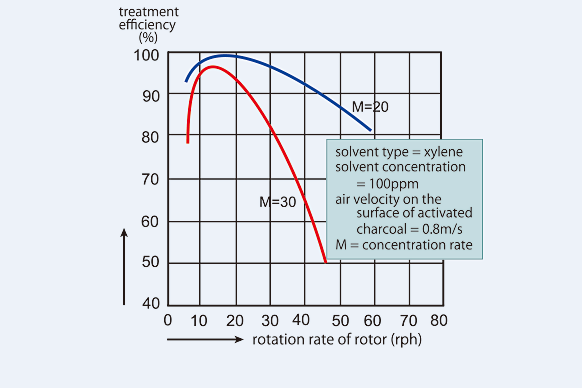 Figure 4. Treatment efficiency of exhaust gas
Figure 4. Treatment efficiency of exhaust gas
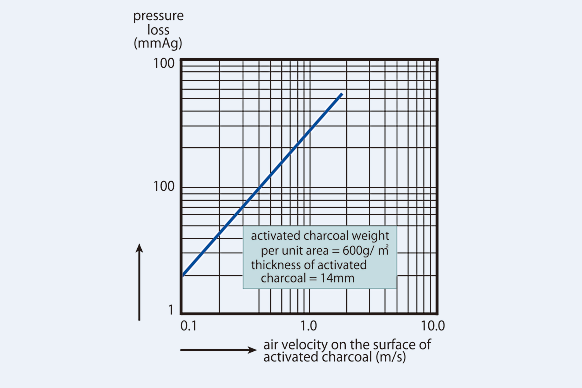 Figure 5. Pressure loss of Admat®(C model)
Figure 5. Pressure loss of Admat®(C model)
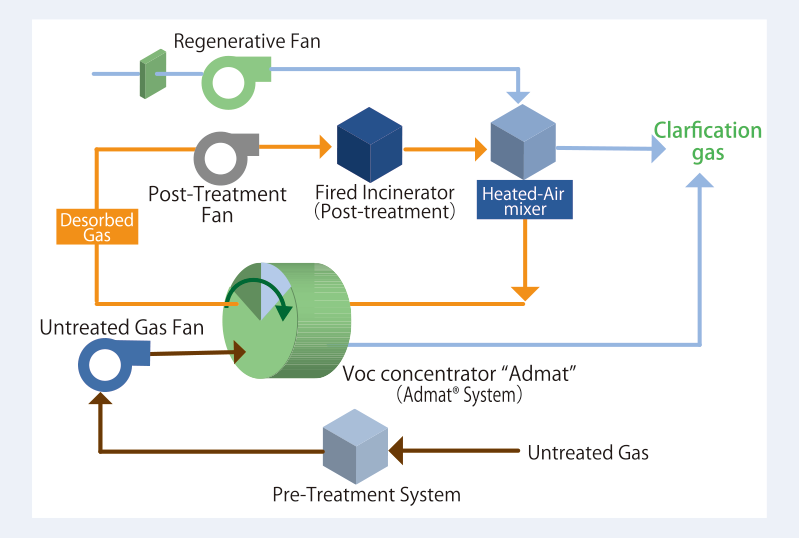
Configuration of Admat® System
Depending on the source of the gas and if needed, dry filters are used to remove mist or dust from untreated gas.
Then, Admat® (concentration unit) repeats the adsorption and desorption process.
The gas concentrated with Admat® is made harmless by recovering the solvent with the post-treatment equipment or using oxidative decomposition (with direct or catalytic combustion).
With the oxidative decomposition method, the waste heat is used as the heat source for desorption.
System Flow Diagram of Admat® System
Adaptive Industrial Sector
Admat® can be effectively used in the industrial sectors listed in the table below.
| Adaptive factories | Pocesses and applications | Target Substance |
|---|---|---|
| Painting | Exhaust from a paint booth; Improvements in working conditions | Paint thinner |
| Printing | Exhaust from a dry kiln, and local exhaust around printers | Thinner for ink |
| Chemical | Exhaust with the organic or cleaning solvents | Organic solvents |
| Food | Exhaust from the manufacturing processes; Improvements in working conditions | Alcohol, etc. |
| Semiconductor | Exhaust from the cleaning and resist application processes | Organic solvents |
| Electronic parts | Exhaust from the cleaning processes | Organic solvents |
| Medicinal chemical | Exhaust from the production of raw materials | Organic solvents |
| Industial machinery | Exhaust from the painting, bonding, and cleaning processes | Paint thinner |
| Others | Improvements in operation and the factory environment | Solvents |
Admat®Z
Overview
The Admat®Z is an absorbent-based air purifying system for organic or cleaning solvents and gas containing malodorous substances in factroies for painting, printing, semiconductors, electronic parts, precision machinery and chemical or for pharmaceutical industries. The hydropholic sysntheic zeolite is used for absorbent.
 The Admat®Z(absorbent:hydropholic sysntheic zeolite)
The Admat®Z(absorbent:hydropholic sysntheic zeolite)
Features
-
Various VOC removal
Admat® Z concentrates VOCs that most activated carbons had limits or problems.
-
Non-flammable rotor
High boiling VOCs treatment is available. Regeneration at high temeperature is enforced with non-flammable and heat resistant rotor with hydrophobic zeolite
-
Capable of wide concentration range
Standard model with a simple duct system is applicable for VOC with an 15 times or less concentration. High-concentration model with additional re-circulation and purge flow bled ducting system is available for higher ratios. Concentrations of 30 times or higher can be handled with the high-concentration model depending on the type of VOC.
Spetifications
Structure of Admat® Z model
Admat® Z uses a honeycomb rotor that supports hydrophobic zeolite. The rotor is comprised of three sectors (treating, regenerating, and purging setor) and repeats the cycle of adsorption, desorption, and cooling (Figure 6) while rotating slowly. VOCs contained in untreated gas exhausted during the production process is adsorbed by the rotor as they pass through the treatment sector. Untreated gas that pass through the treatment sector are released into the atmosphere as clean processed gas.
VOCs adsorbed in the treating sector are desorbed in the regenerating sector by hot air in small amounts at high temperatures (approximately 180℃). The small amount of hot air means that the desorbed VOCs become concentrated exhaust with high density, but low volume. The concentrated exhaust is treated in subsequent processes by an incinerator.
Purging sector is placed after the regenerating sector for cooling rotors with low- temperature air since even the desorption is sufficient, the rotor has lower absorbability of VOC right after the regeneration sector, because of its heat. Cooled rotors are capable of VOCs absorption in the treatment sector again.
If higher concentration ratios are required, they can be handled by the high-concentration model with additional regenerating and purge-flow-bled cycle for the duct system around the rotors for sufficient regeneration and purge (Figure 7).
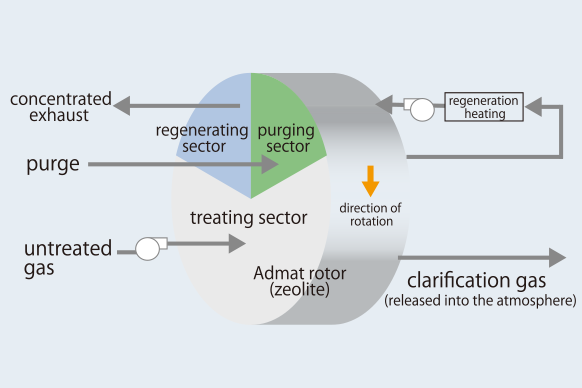 Figure 6. Admat® Z standard model
Figure 6. Admat® Z standard model
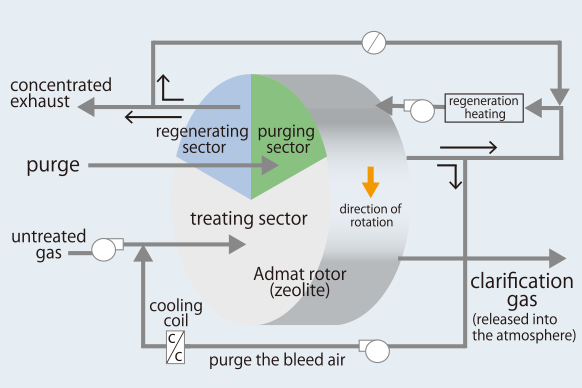 Figure 7. Admat® Z high-concentration model
Figure 7. Admat® Z high-concentration model
Performance of Admat® Z (high-concentration model)
The treatment efficiency of Admat® Z differs depending on the type and concentration of the gas treated (Figure 8). It achieves a high concentration ratio while maintaining high treatment efficiency for low-concentration untreated gas.
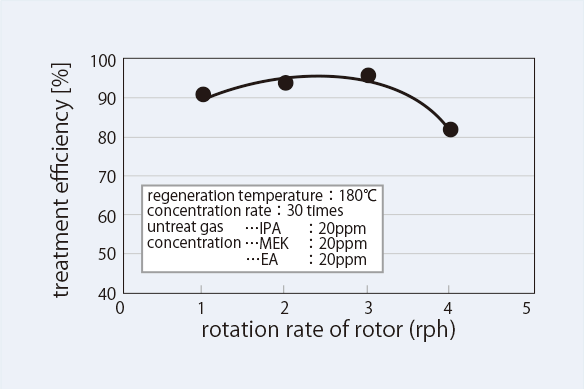 Figure 8. Admat® Z high-concentration model
Figure 8. Admat® Z high-concentration model
Configuration of the VOC treatment system
If needed, dry filters are used to remove mist or dust depending on the source of gas.
Next, Admat® Z adsorbs VOCs contained in untreated gas to release it into the atmosphere as clean processed gas. The adsorbed VOCs are desorbed by hot air in small volumes, turning into concentrated gas.
The gas concentrated with Admat® is made harmless by recovering the solvent with the post-treatment equipment or using oxidative decomposition with direct or catalytic combustion.
When the oxidative decomposition method is applied, the waste heat is utilized for the desorption.
Process flow of Admat®
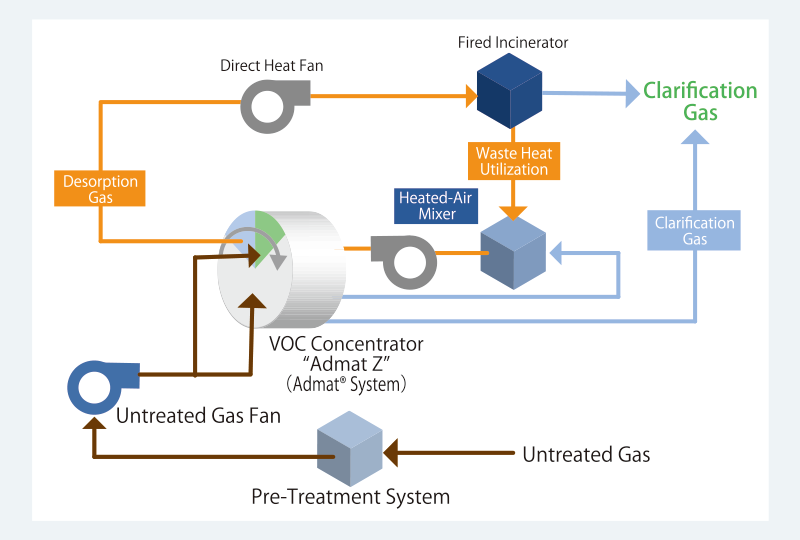 Standard Model Admat® Z
Standard Model Admat® Z
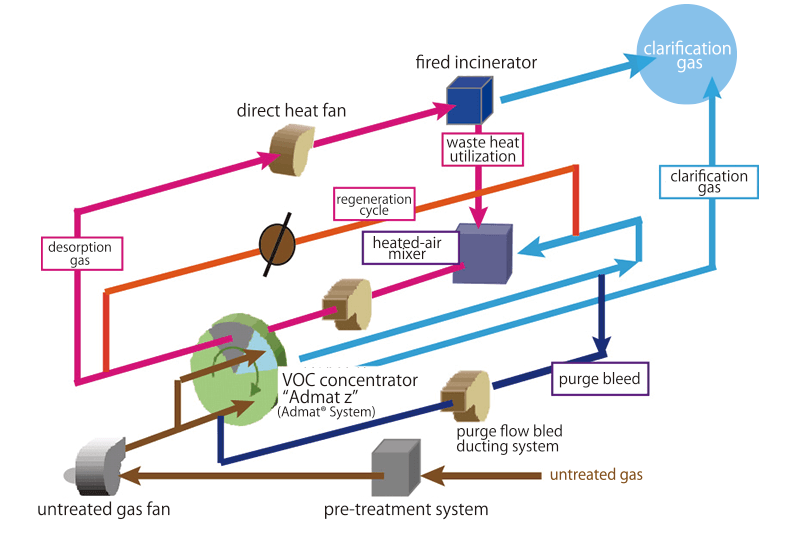 High-concentration Model Admat® Z
High-concentration Model Admat® Z
Adaptive Industrial Sector
Admat Z can be effectively used in the industrial sectors listed in the table below.
| Adaptive factories | Pocesses and applications | Target Substance |
|---|---|---|
| Painting | Exhaust from a paint booth; Improvements in working conditions | Paint thinner |
| Printing | Exhaust from a dry kiln, and local exhaust around printers | Thinner for ink |
| Chemical | Exhaust with the organic or cleaning solvents | Organic solvents |
| Food | Exhaust from the manufacturing processes; Improvements in working conditions | Alcohol, etc. |
| Semiconductor | Exhaust from the cleaning and resist application processes | Organic solvents |
| Electronic parts | Exhaust from the cleaning processes | Organic solvents |
| Medicinal chemical | Exhaust from the production of raw materials | Organic solvents |
| Industial machinery | Exhaust from the painting, bonding, and cleaning processes | Paint thinner |
| Others | Improvements in operation and the factory environment | Solvents |
